AoPS online math classes prepare gifted middle school and high school students for the rigors of top-tier colleges and internationally competitive careers. Mathematics is an excellent vehicle for learning these skills, and problem solving is a wonderful way to develop conceptual understanding and procedural fluency in mathematics. In this course, you will examine the research and reasoning behind the movement to emphasize problem solving as a foundation of mathematics education. Problem solving can be used to motivate students by providing them with interesting situations that represent a challenge and that often relate mathematics to real-life situations. It offers the opportunity to “use knowledge meaningfully” (Marzano and Pickering, 1997, pp. Problem-solving can also be used effectively as a vehicle for. Online math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus, and other math problems. Get help on the web or with our math app.
We have selected relevant material from MIT's introductory courses to support students as they study and educators as they teach the Advanced Placement Calculus curriculum. This section is organized by the topics that you’ll see on the AP* Calculus Exam.
* AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse, this product.
Introductory MIT Courses
The following courses and resources have been selected to help you explore mathematics at MIT.
The first two courses listed below, Single Variable Calculus (18.01SC) and Multivariable Calculus (18.02SC) are in our OCW Scholar format. OCW Scholar courses are designed for study at your own pace. They contain substantially more material than typical OCW courses, blending new content with exiting material used in MIT classes.
/MathStudent-58c1b1935f9b58af5c08ae20.jpg)
Learn more about OCW Scholar.
Calculus Resources

| » Single Variable Calculus (18.01SC) A version of Single Variable Calculus designed especially for self learners. | Prof. David Jerison |
| » Multivariable Calculus (18.02SC) A version of Multivariable Calculus designed especially for self learners. | Prof. Denis Auroux |
| » Highlights of Calculus A series of short videos that introduce the basics of calculus—how it works and why it is important. | Prof. Gilbert Strang |
| » Calculus Revisited: Single Variable Calculus A series of videos and related resources that cover the materials normally found in a freshman-level introductory calculus course. The series was first released in 1970. | Prof. Herbert Gross |
| » Calculus Online Textbook | Prof. Gilbert Strang |
Additional Mathematics Resources
Problem Solving Training
| » Street-Fighting Mathematics (18.098) | Dr. Sanjoy Mahajan |
| » Problem Solving Seminar (18.S34) | Prof. Hartley Rogers, Prof. Kiran Kedlaya, Prof. Richard Stanley |
| » Introduction to MATLAB | Yossi Farjoun |
| » The Mathematics of Toys and Games | Jing Li, Prof. Erik Demaine, Melissa Gymrek |

These courses were offered through the High School Studies Program (HSSP), a project of the MIT Educational Studies Program. HSSP offers non-credit enrichment courses to 7th-12th grade students on weekends at MIT.
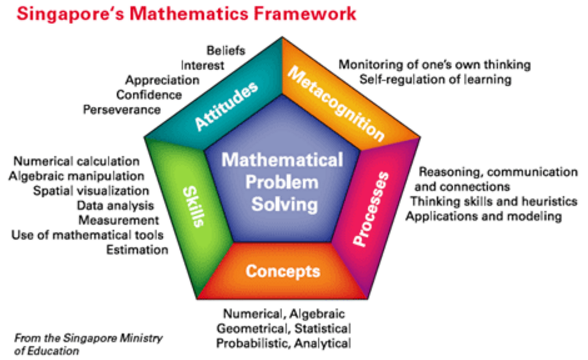
What Is Math Problem Solving
| » Combinatorics: The Fine Art of Counting | Andrew Sutherland |
| » Probability: Random Isn't So Random | Vina Nguyen |
Math Problem Solving Questions
- MATH 0405
Study Skills: Math Anxiety
1 credit hourBasic course designed for students who want to reduce or manage math anxiety. Students examine underlying issues that contribute to math anxiety; discuss various learning styles; assess own learning style; learn ways to accommodate an instructor's teaching style; and learn strategies and techniques to effectively cope with math anxiety. This course may be taken three times for credit. This course can only be taken on a pass/fail basis. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (1 lecture hour)
- MATH 0408
Arithmetic Whole Numbers I
0.5 credit hoursComputation skills involving addition and subtraction of whole numbers and applications. This course can only be taken on a pass/fail basis. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (.5 lecture hour)
- MATH 0409
Arithmetic Whole Numbers II
0.5 credit hoursComputation skills involving multiplication and division of whole numbers and applications. This course can only be taken on a pass/fail basis. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (0.5 lecture hour)
- MATH 0410
Arithmetic of Whole Numbers
0.5 credit hoursComputation skills involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and applications of whole numbers. This course may be taken four times for credit. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (0.5 lecture hour)
- MATH 0412
Arithmetic of Fractions I
0.5 credit hoursComputation skills involving addition and subtraction of fractions and mixed numbers. This course may be taken four times for credit. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (0.5 lecture hour)
- MATH 0413
Arithmetic of Fractions II
0.5 credit hoursComputation skills involving multiplication and division of fractions and mixed numbers. This course may be taken four times for credit. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (0.5 lecture hour)
- MATH 0415
Arithmetic of Decimals
0.5 credit hoursComputation skills involving addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of decimals. This course may be taken four times for credit. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (0.5 lecture hour)
- MATH 0417
Arithmetic of Percents
0.5 credit hoursComputation skills involving percents, conversions among fractions, o decimals and percents including applications. This course may be taken four times for credit. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (0.5 lecture hour)
- MATH 0418
Arithmetic of Ratio/Proportion
0.5 credit hoursComputation skills involving ratio and proportion. This course may be taken four times for credit. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (0.5 lecture hour)
- MATH 0420
Arithmetic: Special Topics
0.5 credit hoursTopics include exponents, roots, rounding and estimating. This course may be taken four times for credit. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (0.5 lecture hour)
- MATH 0422
Arithmetic of Signed Numbers
0.5 credit hoursComputation skills involving addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of signed numbers, and properties of numbers. This course may be taken four times for credit. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (0.5 lecture hour)
- MATH 0424
Algebra: Solving Linear Equations
0.5 credit hoursSolve linear equations algebraically. This course may be taken four times for credit. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (0.5 lecture hour)
- MATH 0426
Algebra: Word Problems
0.5 credit hoursWord problems involving money, ratio and proportion, percent and variation. This course may be taken four times for credit. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (0.5 lecture hour)
- MATH 0428
Algebra: Exponents
0.5 credit hoursAlgebraic expressions involving positive, negative and zero exponents. This course may be taken four times for credit. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (0.5 lecture hour)
- MATH 0430
Algebra: Factoring
0.5 credit hoursFactoring polynomials and its application in solving equations. This course may be taken four times for credit. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (0.5 lecture hour)
- MATH 0432
Algebra: Fractions
0.5 credit hoursComputation skills involving addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of algebraic fractions and applications of algebraic fractions. This course may be taken four times for credit. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (0.5 lecture hour)
- MATH 0434
Algebra: Graphing
0.5 credit hoursGraph linear and quadratic equations and linear inequalities. This course may be taken four times for credit. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (0.5 lecture hour)
- MATH 0436
Algebra: Systems of Linear Equations
0.5 credit hoursSolving systems of linear equations including applications by graphing, elimination and substitution. This course may be taken four times for credit. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (0.5 lecture hour)
- MATH 0438
Algebra: Radicals
0.5 credit hoursSimplifying algebraic expressions containing radicals by addition, subtraction, multiplication and division; radical equations; Pythagorean Theorem applications. This course may be taken four times for credit. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (0.5 lecture hour)
- MATH 0440
Algebra: Quadratic Equations
0.5 credit hoursSolve quadratic equations by factoring and the quadratic formula. This course may be taken four times for credit. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (0.5 lecture hour)
- MATH 0451
Essentials of Arithmetic I
2 credit hoursFundamental skills in addition, subtraction, multiplication and division with respect to whole numbers, fractions, ratio and proportion, and decimals. Included are problem-solving techniques with practical application. Equivalent to the first half of Mathematics 0460. This course may be taken four times for credit. (2 lecture hours)
- MATH 0452
Essentials of Arithmetic II
2 credit hoursPrinciples of arithmetic, review of fractions, exponents, order of operations, percents and applications, ratio and proportion, and applications. This course may be taken four times for credit. (2 lecture hours)
- MATH 0455
Fundamentals of Algebra
2 credit hoursCovers essential fundamentals of algebra. Students begin with signed numbers, learn to solve equations and inequalities, apply properties of exponents, and perform fundamental operations with polynomials. Included are problem-solving techniques with practical application. This course may be taken four times for credit. (2 lecture hours)
- MATH 0459
Whole Number Arithmetic
1 credit hourContent includes principles of arithmetic: fundamental operations with whole numbers, common fractions, decimals, exponents, roots, and order of operations. Prerequisite: A qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (2 lab hours)
- MATH 0460
College Arithmetic
3 credit hoursPrinciples of arithmetic. Fundamental operations with whole numbers, common fractions and decimals. Percents and applications in the world of business. Rational numbers, exponents and powers. This course may be taken four times for credit. (3 lecture hours)
- MATH 0461
Pre-Algebra
3 credit hoursContent includes principles of arithmetic: fundamental operations with whole numbers, common fractions, decimals, percents and applications in the world of business, rational numbers, exponents, and powers. Prerequisite: Mathematics 0459 with a C or better, or equivalent, or qualifying score on placement exam. (3 lecture hours)
- MATH 0465
Preparatory Mathematics for General Ed
5 credit hoursStudents develop the foundational mathematical skills necessary for general education mathematics courses (Math 1218 and Math 1220). Content features collaborative project-based and technology-enabled group work including modeling, problem solving, critical thinking, data analysis, algebra fundamentals, and both verbal and written communication of mathematical ideas. Prerequisite: Mathematics 0461 with a grade of C or better, or equivalent or Mathematics 0481 with a grade of C or better, or equivalent or a qualifying score on the math placement exam. (5 lecture hours)
- MATH 0470
Elementary Plane Geometry
3 credit hoursPoints and lines in the plane, angles, triangles, quadrilaterals, polygonal regions, circles and their relationships. Prerequisite: Mathematics 0481 or college equivalent with a grade of C or better or a qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (3 lecture hours)
- MATH 0481
Foundations for College Mathematics I
5 credit hoursTopics from elementary algebra: sets of numbers, operations with real numbers, variables, integral exponents, scientific notation, simplification of algebraic expressions, solving linear equations and inequalities in one variable, graphing linear equations, writing equations of lines, solving linear inequalities in two variables, solving systems of linear equations in two or more variables, applications, problem solving, operations with polynomials, factoring polynomials, and solving equations using factoring. Prerequisite: Mathematics 0460 with a grade of C or better, or equivalent or Mathematics 0461 with a grade of C or better, or equivalent or a qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (5 lecture hours)
- MATH 0482
Foundations for College Mathematics II
5 credit hoursStudents will survey topics from elementary algebra and intermediate algebra. Topics include: operations with algebraic fractions, solving equations with the algebraic fractions, radicals and rational exponents, complex numbers, solving quadratic equations, variation, solving equations and inequalities involving absolute value, function notation, graphing functions, inverse functions, exponential and logarithmic functions, applications, and problem solving. Prerequisite: Demonstrated geometry competency (level 2) and Mathematics 0481 (or college equivalent)with a grade of C or better or a qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (5 lecture hours)
- MATH 0485
Algebra Refresher Workshop
0.5 credit hoursDesigned as a focused review of the elementary and intermediate algebra techniques and associated problem solving skills required for a student to be successful in college level math. Students meeting mastery-level performance qualifications in the workshop can take a written departmental exit examination for potential placement. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (0.5 lecture hour)
- MATH 1100
Business Mathematics
3 credit hoursStudents will be introduced to the application of mathematics to business transactions, analysis and solution of the business problems in profit and loss, interest, installment transactions, percent discounts, taxes, and payroll. Prerequisite: Mathematics 0460 with a grade of C or better, or equivalent or Mathematics 0461 with a grade of C or better, or equivalent or a qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (3 lecture hours)
- MATH 1102
Mathematics for Health Sciences
3 credit hoursDesigned for health science majors. Topics include systems of measurements, use of formulas, dimensional analysis, percents, decimals, fractions, ratio and proportion, direct and inverse variation, solutions, and dosage calculations. Prerequisite: Mathematics 0465 or Mathematics 0481 or college equivalent with a grade of C or better or a qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (3 lecture hours)
- MATH 1104
Mathematics for Horticulture
3 credit hoursDesigned for horticulture majors only. Topics include fractions, decimals, percents, systems of measurement, dimensional analysis, use of formulas, ratio and proportion, linear equations, perimeter, area, volume, and surface area as related to landscape, mixtures as related to seed, fertilizer and chemicals, estimation, scale drawings, sales including discount and markup, construction as related to landscape, and estimates and bids on landscaping projects. (3 lecture hours)
- MATH 1108
Perspectives of Mathematics
3 credit hoursThe course surveys some of the major ideas of mathematics and relationships to the arts, life sciences, physical sciences, social sciences, games, etc. Topics are selected from number systems, inductive and deductive reasoning, algebraic processes and methods, geometry, probability and statistics. Prerequisite: Demonstrated geometry competency (level 2), and Mathematics 0481 or college equivalent with a grade of C or better or a qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (3 lecture hours)
- MATH 1115
Technical Mathematics I
3 credit hoursFor technical/occupational programs. Emphasizes problem-solving skills using elementary algebra, right angle trigonometry, and ratio and proportion. Prerequisite: Mathematics 0481 or college equivalent with a grade of C or better or a qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (3 lecture hours)
- MATH 1116
Technical Mathematics II
5 credit hoursA continuation of Technical Mathematics I emphasizing problem solving-skills using trigonometry, common logarithms and natural logarithms. Prerequisite: Mathematics 1115 with a grade of C or better. (5 lecture hours)
- MATH 1120
Mathematical Foundations for Diagnostic
3 credit hoursStudents will be introduced to mathematical applications and problem solving in the field of sonography. Topics include systems of measurement, dimensional analysis, application of formulas, probability, and statistics. Curriculum is designed for ultrasound program applicants. Prerequisite: Mathematics 0482 (or college equivalent) with a grade of C or better or a qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (3 lecture hours)
- MATH 1218 (IAI M1 904)
General Education Mathematics
3 credit hoursStudents will learn mathematical reasoning and the solving of real-life problems, rather than routine skills. Four topics will be studied: set theory, logic theory, counting techniques and probability, and mathematics of finance. The course is designed to fulfill general education requirements, and not designed as a prerequisite for any other college mathematics course. Prerequisite: Mathematics 0465 or Mathematics 0482 or college equivalent with a grade or C or better or a qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (3 lecture hours)
- MATH 1220 (IAI M1 901)
Quantitative Literacy
3 credit hoursStudents will learn basic numeracy needed by a college graduate to reason about quantities, their magnitudes, and their relationships between and among other quantities. Topics include linear systems, linear programming, analysis and interpretation of graphs, logic and reasoning, descriptive statistics, the normal distribution, statistical inference, estimation, and approximation. This course is designed to fulfill general education requirements, and not designed as a prerequisite for any other college mathematics course. Prerequisite: Mathematics 0465 or Mathematics 0482 or college equivalent with a grade of C or better or a qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (3 lecture hours)
- MATH 1321
Math for Elementary School Teachers I
4 credit hoursStudents interested in a career working with children from birth to grade 8 would benefit from taking this course. Students will explore sets, logic and mathematical reasoning, problem solving, numeration systems, and elementary number theory. Other topics will include properties, algorithms, and computation with the sets of whole numbers, integers, and rational and real numbers. Prerequisite: Demonstrated geometry competency (level 1), and Mathematics 0482 or college equivalent with a grade or C or better or a qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (4 lecture hours)
- MATH 1322 (IAI M1 903)
Math for Elementary School Teacher II
3 credit hoursA continuation of Mathematics 1321. Designed for elementary education majors. Introduction to probability and statistics, measurement, geometric constructions, coordinate geometry and geometric transformations. Prerequisite: Mathematics 1321 or college equivalent with a grade of C or better and demonstrated geometry competency (level 1). (3 lecture hours)
- MATH 1340
History of Mathematics
3 credit hoursThe historical development of mathematics and certain mathematical concepts from ancient times to the present, with emphasis given to basic and intermediate mathematics concepts. The focus of this mathematics-driven course will be on the problems mathematicians have faced, and the theory and methodology that were developed to resolve these problems. Prerequisite: Mathematics 1218 or college equivalent with a grade of C or better. (3 lecture hours)
- MATH 1428
College Algebra With Applications
3 credit hoursStudents will learn algebra with an emphasis on applications. This course should not be taken by students planning to enroll in calculus. Topics include, but are not limited to, matrices, functions, conic sections, polynomials, exponential and logarithmic functions, and sequences and series. Prerequisite: Demonstrated geometry competency(level 2), and Mathematics 0482 or college equivalent with a grade or C or better or a qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (3 lecture hours)
- MATH 1431
Precalculus I
5 credit hoursStudents will learn algebra with an emphasis on concepts needed for calculus. Topics include, but are not limited to, functions, conic sections, matrices and determinants, polynomial theory, rational functions, sequences and series, logarithmic and exponential functions, combinatorial mathematics, and mathematical induction. Prerequisite: Demonstrated geometry competency (level 2), and Mathematics 0482 or college equivalent with a grade or C or better or a qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (5 lecture hours)
- MATH 1432
Precalculus II/Trigonometry
3 credit hoursStudents will learn trigonometry with an emphasis on concepts needed for calculus. Topics include, but are not limited to, formal definition of trigonometric functions and circular functions, radian measure, inverse trigonometric functions, graphs of trigonometric functions and inverse trigonometric functions, trigonometric identities, trigonometric equations, DeMoivre's theorem, solution of triangles, polar coordinates, and applications. Prerequisite: Mathematics 1431 or college equivalent with a grade of C or better or a qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (3 lecture hours)
- MATH 1533 (IAI M1 906)
Finite Mathematics
4 credit hoursStudents will be introduced to sets, counting techniques, probability, modeling, systems of linear equations and inequalities, matrix algebra, linear programming, Markov chains, and game theory. This course is intended for students planning to major in business, or the behavioral, social, or biological sciences. Prerequisite: Mathematics 1428 or college equivalent with a grade of C or better or Mathematics 1431 or college equivalent with a grade of C or better or a qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (4 lecture hours)
- MATH 1635 (IAI M1 902/BUS 901)
Statistics
4 credit hoursStudents will be introduced to elements of descriptive and inferential statistics. Topics include communication with data descriptions and graphs; probability principles and their use in developing probability distributions; binomial, normal, student-t, chi-square, and F distributions; hypothesis testing; estimation; contingency tables; linear regression and correlation; and one-way ANOVA. Prerequisite: Mathematics 1428 or college equivalent with a grade of C or better or Mathematics 1431 or college equivalent with a grade of C or better or Mathematics 1533 or college equivalent with a grade of C or better or a qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (4 lecture hours)
- MATH 1820
Selected Topics I
1 to 3 credit hoursIntroductory exploration and analysis of selected mathematics topics with a specific theme indicated by course title listed In college class schedule. May be taken three times for credit as long as different topics are selected. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. The precise prerequisites will vary according to the specific mathematical selected topic. (1 to 3 lecture hours)
- MATH 1840
Independent Study
1 to 4 credit hoursExploration and analysis of topics within Mathematics to meet individual student-defined course description, goals, objectives, topical outline and methods of evaluation in coordination with and approved by the instructor. This course may be taken four times for credit as long as different topics are selected. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. (1 to 4 lecture hours)
- MATH 2000 (IAI M1 900-O)
Survey of Calculus
3 credit hoursStudents will study functions, limits, continuity, the derivative, rules for differentiation of algebraic, trigonometric, and the transcendental functions, anti-derivatives and integration, the fundamental theorem of calculus, and techniques of integration. Note: Students may not receive credit for Math 2000 and Math 2134 or Math 2231 or Math 2232. Prerequisite: Mathematics 1431 or college equivalent with a grade of C or better and Mathematics 1432 or college equivalent with a grade of C or better or a qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (3 lecture hours)
- MATH 2115 (IAI M1 905/CS 915)
Discrete Mathematics
3 credit hoursStudents will be introduced to the formal study of discrete structures in mathematics. Topics include set theory, combinatorial mathematics, logic, graph theory, Boolean algebra, and formal languages. Prerequisite: Mathematics 1428 or college equivalent with a grade of C or better or Mathematics 1431 or college equivalent with a grade of C or better or a qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (3 lecture hours)
- MATH 2134 (IAI M1 900-B)
Calculus for Business and Social Science
4 credit hoursStudents will be introduced to basic concepts of differential and integral calculus. This course is intended for students planning to major in business, or the behavioral, social, or biological sciences. Prerequisite: Mathematics 1431 or college equivalent with a grade of C or better or a qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (4 lecture hours)
- MATH 2231 (IAI M1 900-1/MTH901)
Calculus and Analytic Geometry I
5 credit hoursThis is the first calculus course for students majoring in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. Topics include lines, circles, functions, limits, continuity, the derivative, rules for differentiation of algebraic, trigonometric, and the transcendental functions, related rates, mean value theorem, optimization and curve sketching, differentials, Newton's method, antiderivatives and integration, and the fundamental theorem of calculus. Prerequisite: Mathematics 1431 or college equivalent with a grade of C or better and Mathematics 1432 or college equivalent with a grade of C or better or a qualifying score on the mathematics placement test. (5 lecture hours)
- MATH 2232 (IAI M1 900-2/MTH902)
Calculus and Analytic Geometry II
5 credit hoursApplications of the definite integral, techniques of integration, indeterminate forms, improper integrals, sequences and series, Taylor and Maclaurin expansions, power series, conics, parametric equations, polar coordinates, introduction to vectors, and operations on vectors. Prerequisite: Mathematics 2231 with a grade of C or better (5 lecture hours)
- MATH 2233 (IAI M1 900-3/MTH903)
Calculus and Analytic Geometry III
4 credit hoursGeometry of space, cylindrical and spherical coordinate systems, vector functions with physics applications, arc length, curvature, multivariate functions, partial derivatives, multiple integrals and their applications, vector fields and their applications, line integrals and their applications, and Green's theorem in the plane. Prerequisite: Mathematics 2232 with a grade of C or better. (4 lecture hours)
- MATH 2235
Additional Topics in Vector Calculus
1 credit hourAn extension of Calculus III, covering the curl of a vector field, surface integrals, Stoke's theorem, and the divergence theorem. Prerequisite: Mathematics 2233 with a grade of C or better (or college equivalent). (1 lecture hour)
- MATH 2245 (IAI MTH 911)
Linear Algebra
4 credit hoursGeometric vectors and vector spaces, matrices and linear transformations, inner product spaces, eigenvalues and eigenvectors, the determinant function, and formal methods of mathematical proof. Prerequisite: Mathematics 2232 or equivalent with a grade of C or better. (4 lecture hours)
- MATH 2270 (IAI MTH 912)
Differential Equations
4 credit hoursEquations of first order with applications, homogeneous linear equations of higher order with constant coefficients, non-homogeneous linear equations of higher order with constant coefficients, Laplace transform methods, applications of higher order differential equations, linear equations with variable coefficients, power series solutions, systems of linear equations, and numerical solutions of first order equations. Prerequisite: Mathematics 2233 with a grade of C or better. (4 lecture hours)
- MATH 2300
Mathematical Proof
3 credit hoursThis course serves as a transition to upper level mathematics with a focus on writing proofs. Topics include: propositional logic, predicate logic, set theory, mathematical induction, number theory, relations and functions. Prerequisite: Mathematics 2232 with a grade of C or better. (3 lecture hours)
- MATH 2820
Advanced Selected Topics I
1 to 3 credit hoursAdvanced exploration and analysis of selected mathematical topics with a specific theme indicated by course title listed in college class schedule. This course may be taken three times for credit as long as different topics are selected. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor is required. The precise prerequisites will vary according to the specific mathematical selected topic. (1 to 3 lecture hours)
- MATH 2860
Internship (Career & Technical Ed)
1 to 4 credit hoursCourse requires participation in Career and Technical Education work experience with onsite supervision. Internship learning objectives are developed by student and faculty member, with approval of employer, to provide appropriate work-based learning experiences. Credit is earned by working a minimum of 75 clock hours per semester credit hour, up to a maximum of four credits. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor and 2.0 cumulative grade point average; 12 semester credits earned in a related field of study; students work with Career Services staff to obtain approval of the internship by the dean from the academic discipline where the student is planning to earn credit.
- MATH 2865
Internship Advanced (Career & Tech Ed)
1 to 4 credit hoursContinuation of Internship (Career and Technical Education). Course requires participation in Career & Technical Education work experience with onsite supervision. Internship learning objectives are developed by student and faculty member, with approval of employer, to provide appropriate work-based learning experiences. Credit is earned by working a minimum of 75 clock hours per semester credit hour, up to a maximum of four credits. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor and 2.0 cumulative grade point average; 12 semester credits earned in a related field of study; students work with Career Services staff to obtain approval of the internship by the dean from the academic discipline where the student is planning to earn credit.
- MATH 2870
Internship (Transfer)
1 to 4 credit hoursCourse requires participation in work experience with onsite supervision. Internship learning objectives are developed by student and faculty member, with approval of employer, to provide appropriate work-based learning experiences. Credit is earned by working a minimum of 75 clock hours per semester credit hour, up to a maximum of four credits. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor and 2.0 cumulative grade point average; 12 semester credits earned in a related field of study; students work with Career Services staff to obtain approval of the internship by the dean from the academic discipline where the student is planning to earn credit.
- MATH 2871
Internship - Advanced (Transfer)
1 to 4 credit hoursContinuation of Internship (Transfer). Course requires participation in work experience with onsite supervision. Internship learning objectives are developed by student and faculty member, with approval of employer, to provide appropriate work-based learning experiences. Credit is earned by working a minimum of 75 clock hours per semester credit hour, up to a maximum of four credits. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor and 2.0 cumulative grade point average; 12 semester credits earned in a related field of study; students work with Career Services staff to obtain approval of the internship by the dean from the academic discipline where the student is planning to earn credit.
